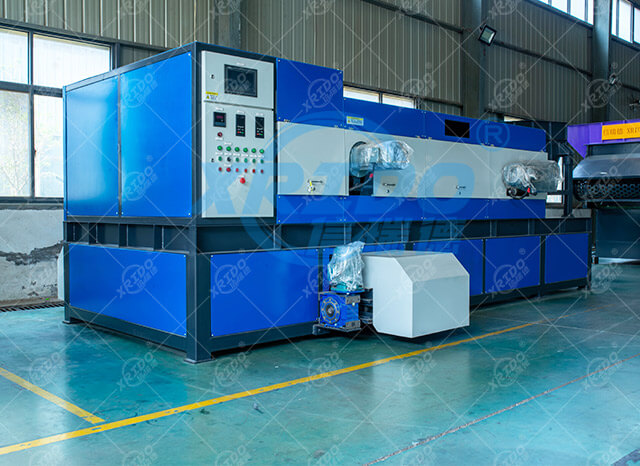
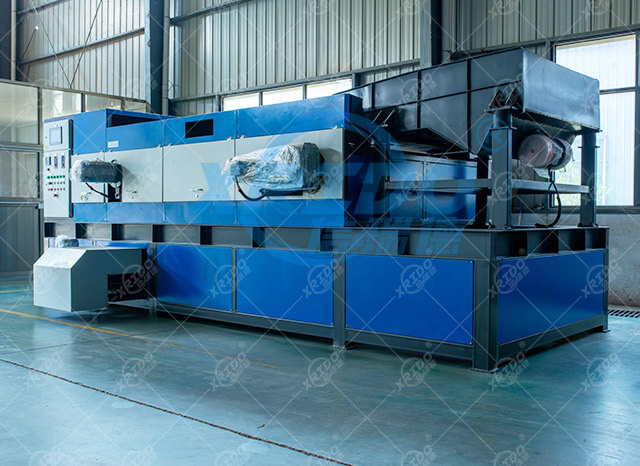
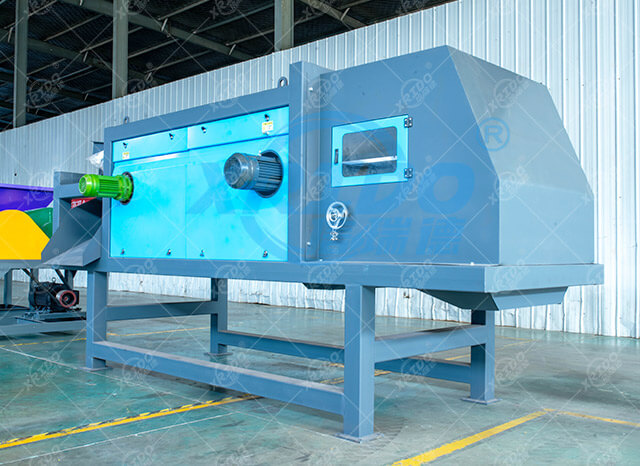
Working principle
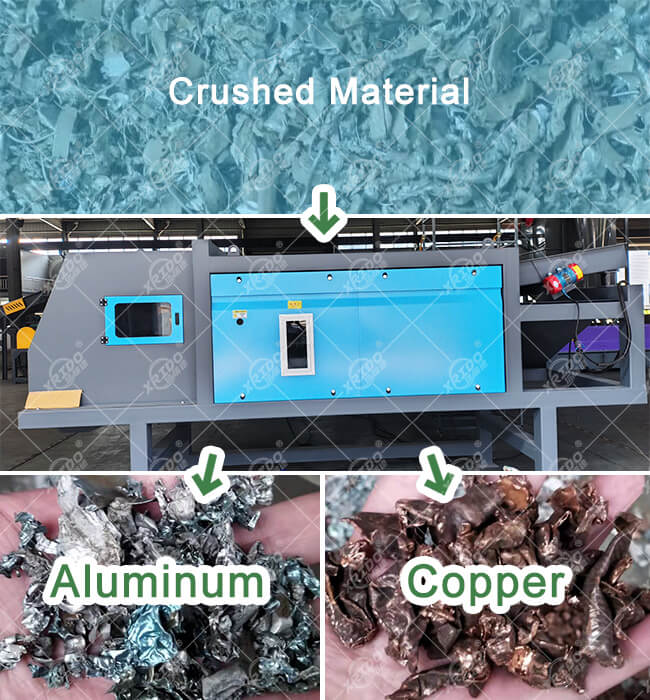
Eddy current separators are based on the principles of electromagnetic induction and the Lorentz force effect. They use an alternating magnetic field to generate eddy currents in conductive metals (especially non-ferromagnetic metals such as aluminum and copper). The resulting opposing magnetic field separates metals from non-metals.
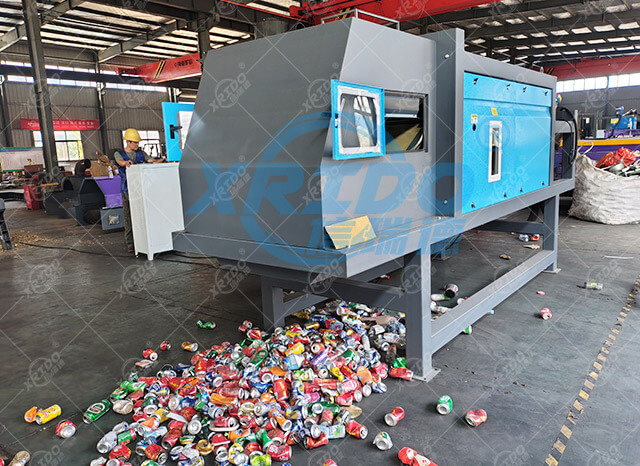

Appliance
Eddy current separators are primarily used to separate non-ferrous metals from mixed waste, shredded materials, or industrial waste. They are particularly suitable for processing the following materials:
- Separating non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, and zinc scrap from non-metals such as plastics, rubber, and glass;
- Sorting aluminum wheels, copper wire, and zinc components from scrapped automobiles;
- Separating non-ferrous metals from scrapped household appliances (such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines);
- Recovering copper, aluminum, and other metals from electronic waste (circuit boards, connectors, etc.);
- Sorting small amounts of non-ferrous metals from household waste, incinerator slag, and industrial solid waste;
- Removing metals from refuse-derived fuel (RDF) production lines;
- Removing scrap from aluminum profile processing plants;
- Separating aluminum and copper from scrap from metal foundries and die-casting plants;
- Removing metal impurities from plastic recycling;
- Removing metallic foreign matter from glass recycling;
- Removal of wire and iron from rubber tire shreds (usually magnetic separation followed by eddy current separation).

Eddy Current Separator
Eddy Current Separator
Video
Eddy Current Separator
The production line can be customized based on actual materials and processing volume.
Advantage
Parameters
| Model | Magnetic roller (φ) | Capacity (T/H) | Power (kw) | Size (mm) |
| XRD400 | 300 | 1-2 | 3+0.55+0.25 | 2885*1500*1693 |
| XRD600 | 300 | 2-4 | 4+0.75+0.25 | 2885*1700*1695 |
| XRD800 | 300 | 5-6 | 5.5+1.1+0.55 | 2950*1900*1695 |
| XRD1000 | 300 | 8-10 | 7.5+1.5+0.55 | 2950*2100*1695 |










